
| Messier 51 |
 |
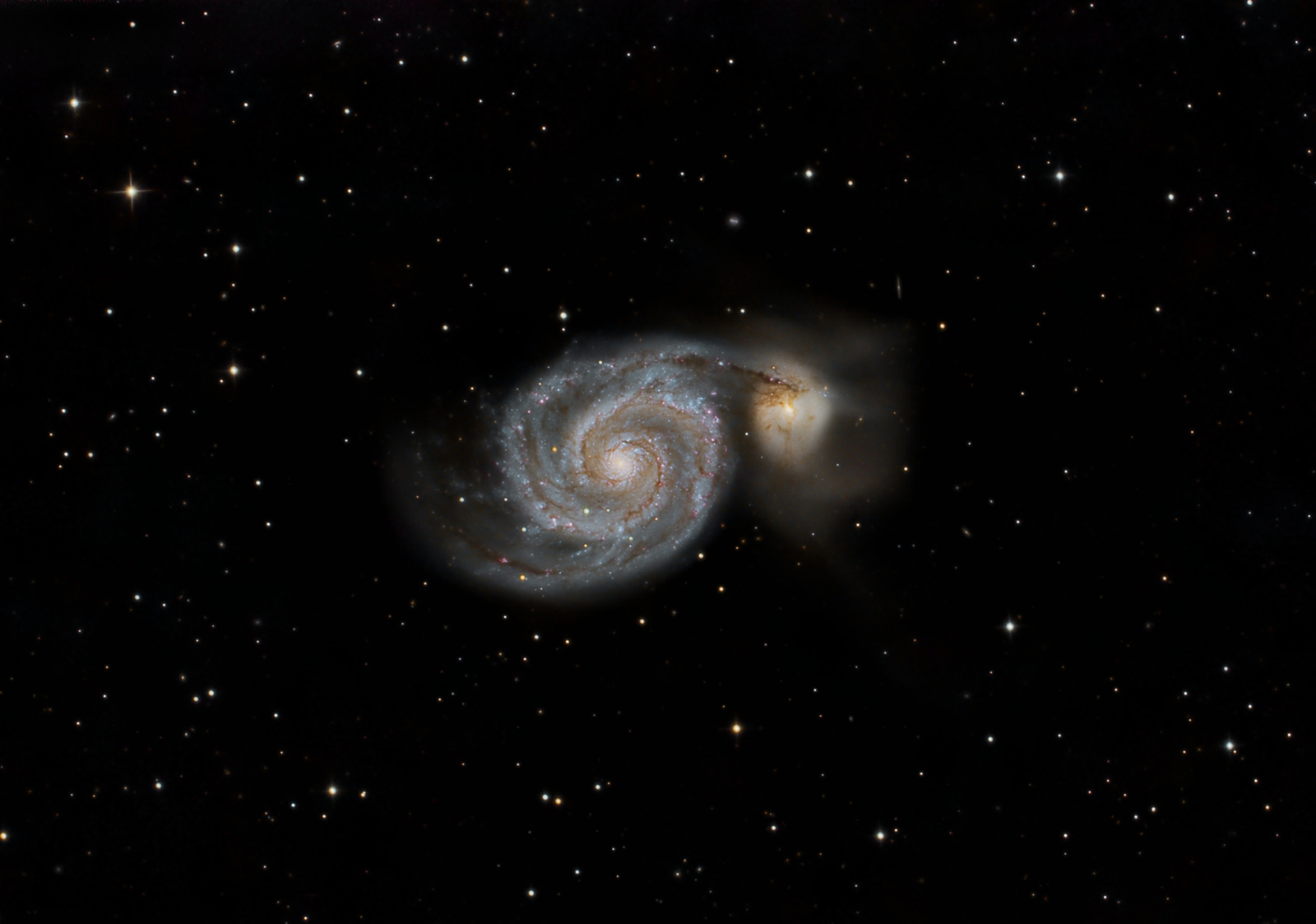
The Whirlpool Galaxy (also known as Messier
51a, M51a, or NGC 5194) is an interacting spiral galaxy that
is estimated to be 23 ± 4 million light-years from the Milky Way Galaxy in the
constellation Canes Venatici. It is one of the most famous galaxies in the sky.
The galaxy and its companion (NGC 5195) are easily observed by amateur
astronomers, and the two galaxies may even be seen with binoculars. The
Whirlpool Galaxy is also a popular target for professional astronomers, who
study it to further understand galaxy structure (particularly structure
associated with the spiral arms) and galaxy interactions. Recently, M51
has been home to two different supernovae in its spiral arms, in 2005 (see image
below), and again most recently in 2011. M51's bright circular disk as a
diameter of approximately 43,000 light-years, and a mass of 160 billion Suns.
M51 is visible through binoculars under dark sky conditions and can be resolved in detail with modern amateur telescopes. When seen through a 4 inch telescope, the basic outlines of M51 and its companion are visible. Under dark skies, and with a moderate eyepiece through a 6 inch telescope, M51's intrinsic spiral structure can be detected. With larger (>12 inch) instruments under dark sky conditions, the various spiral bands are apparent with HII regions visible, and M51 can be seen to be attached to M51B.
Image information courtesy of Wikipedia.
Image Details:
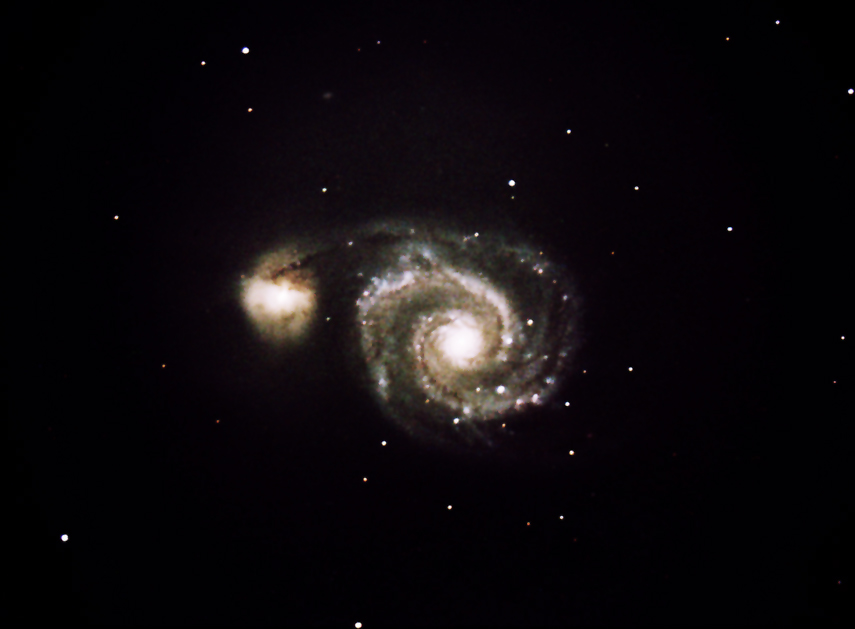
Earlier Images of M51 Below including Supernova Discovery

|
Image
Details:
![]()
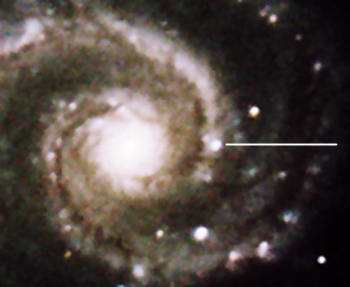 |
| Supernova 2005cs, in one of the spiral arms of M51, discovered on June 27th, 2005, by Wolfgang Kloehr: (Image taken July 2nd, 2005, at 23:50 CDT) |
Page Last Updated: 7/30/2022
wcv